Mineralogical data with the highest accuracy
X-Ray Diffraction is the ideal tool for the basic and the advanced quantitative mineralogical characterization of materials. For Quantitative Phase Analysis (QPA), the results are strongly laboratory dependent. Large deviations from the true phase composition of samples are not uncommon in reports from most (large commercial) laboratories. Qminerals has optimized the preparation and data treatment procedures to ensure optimal quality and reproducibility of XRD spectra.
For the interpretation, Qmineral has developed its own method of which the robustness and accuracy was rewarded the 1st place in the Reynolds Cup round robin for quantitative mineralogy (edition 2016 – aka “the world championship of quantitative mineralogy”). Out of 81 commercial and academic laboratories, Qmineral submitted the most accurate results for 3 unknown mineral mixtures.
XRD analysis can be used for the identification or quantification of
- Natural rocks, sediments and soils, primary raw materials, reservoirs and seals
- Secondary raw materials, cement, plaster, fly ash, bottom ash, slag
- Core material, cuttings, powders, coatings, scalings, dust, filtrates, suspended solids
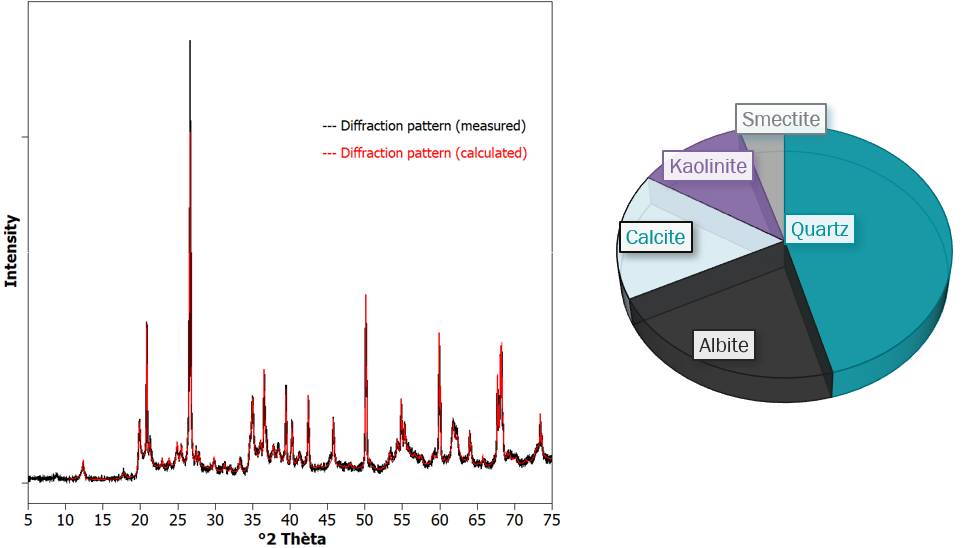
Figure. Quantification of the measured diffraction pattern (black) based on the calculated pattern (red).
Applications
- Reservoir, host rock, seal characterization
- Quantification of crystalline and amorphous phases
- Analysis of clay content, swelling clays, detailed clay mineral analysis
- Analysis of Fe and Mg-contents in Dolomite / Ankerite
- Distinction between CaSO4 varieties (gypsum, bassanite, anhydrite)
- Distinction between TiO2 polymorphs (anatase, rutile, brookite)
- Mineralogy of cements, mortars, binders, concrete, aggregates
- Fly ash, bottom ash, furnace slag characterization
- Calcined clay characterization
- Quantification of crystalline silica and amorphous silica
